Source: Wikimedia Commons
The Warning Signs: What Are These Tiny Red Dots?
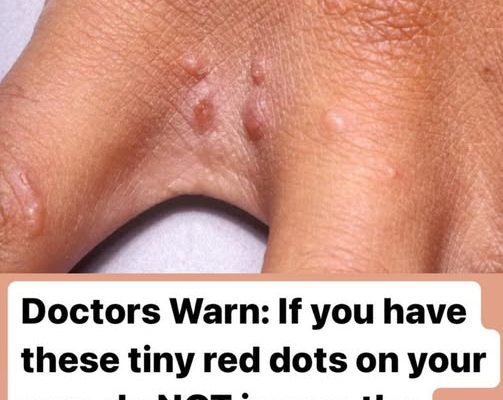
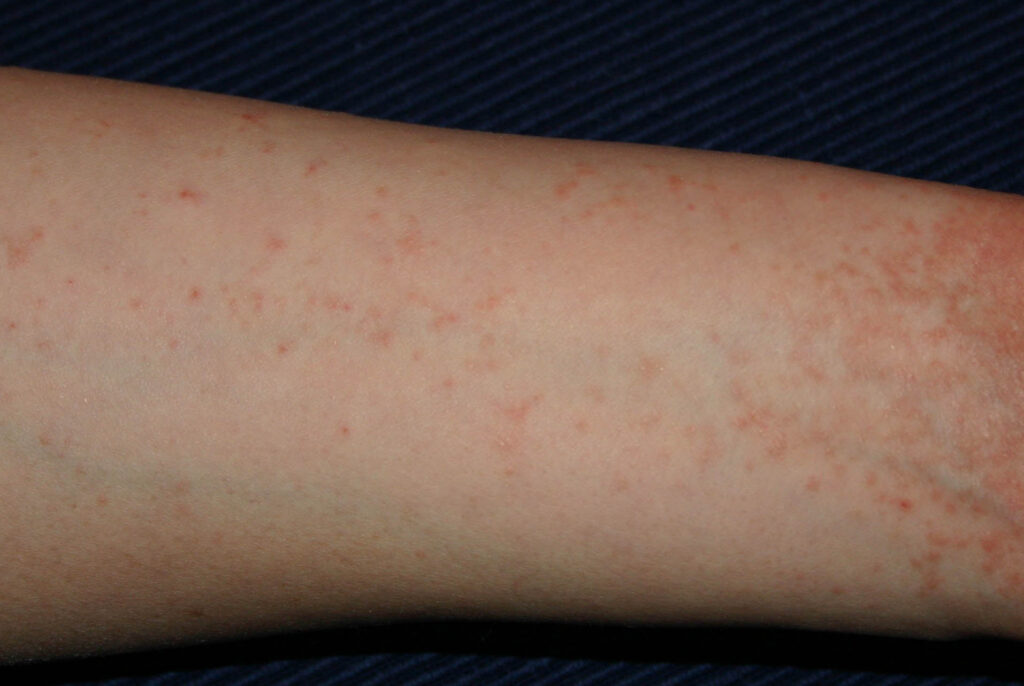
Tiny red dots on your skin could indicate a range of conditions, but one alarming possibility is scabies. Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by mites that burrow under the skin’s surface, laying eggs and causing irritation. While the condition is not life-threatening, it can be extremely uncomfortable, leading to severe itching and rashes.
Doctors are particularly concerned about recent outbreaks in the UK, where there has been a 100% increase in reported cases. The highest incidence has been observed in northern England, with symptoms that often include headaches, limb pain, and diarrhea, alongside the appearance of these red dots.
What Is Scabies and How Does It Spread?
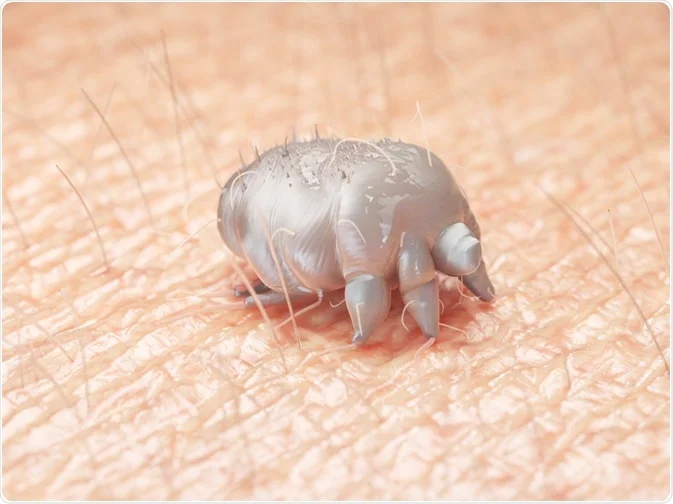
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, a tiny parasite that burrows into the upper layers of the skin, creating tunnels where it lays eggs. These mites are microscopic and cannot be seen with the naked eye, but their presence can result in a range of symptoms, including:
- Intense itching that worsens at night
- Small red bumps or dots on the skin, often around the hands, wrists, elbows, and other warm, folded areas
- Rashes that spread quickly
The condition is highly contagious and spreads through prolonged skin-to-skin contact. This makes it easy to transmit within families, crowded environments, or places with high social interaction, like schools, dormitories, and care facilities. Additionally, sharing clothing, bedding, or towels with an infected person can facilitate the spread of scabies.
How to Recognize Scabies Symptoms: When to Seek Medical Help
Early detection of scabies is crucial to preventing further spread and avoiding complications. So, how can you tell if the tiny red dots on your skin are due to scabies?
1. Persistent Itching
The primary symptom of scabies is intense itching, particularly at night. If you notice itching that seems to get worse at bedtime or after taking a hot shower, it could be an indication of scabies mites becoming more active.
2. Rash and Red Bumps
The rash caused by scabies is characterized by red bumps, which often appear in clusters. These bumps are usually found around the wrists, hands, elbows, or between fingers—places where the skin is warm and conducive for mite activity.
3. Skin Sores and Inflammation
In more severe cases, scratching the itchy areas can lead to open sores and secondary bacterial infections. If you observe signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, or pus, it’s essential to seek immediate medical care.
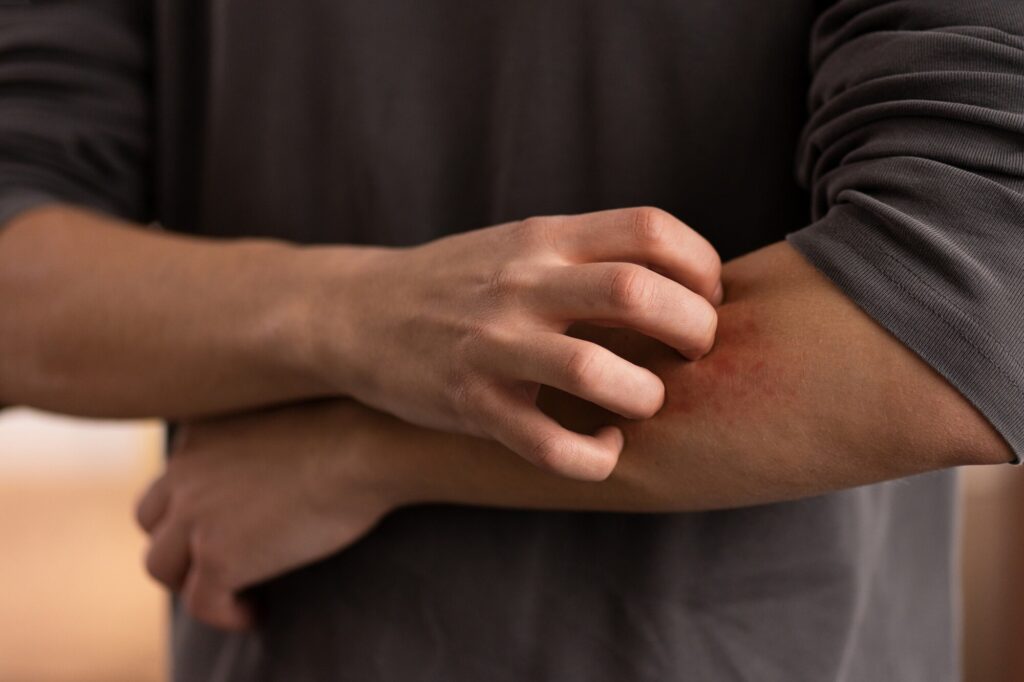

Source: Freepik
High-Risk Groups: Who Is Most Vulnerable to Scabies?
Certain groups are more susceptible to scabies due to close physical contact or shared living conditions. The following populations are at higher risk:
1. School-Age Children and Young Adults
Due to frequent social interactions and physical contact, schoolchildren and college students are at greater risk of contracting scabies. Outbreaks are common in schools, where students often share spaces, supplies, and occasionally clothing or sports equipment.
2. People with Multiple Sexual Partners
Scabies can be sexually transmitted, so individuals with multiple sexual partners are at increased risk. Intimate contact creates an opportunity for mites to transfer from one person to another.
3. Residents of Crowded Living Facilities
Scabies outbreaks are prevalent in settings like nursing homes, prisons, and refugee camps, where people live in close quarters. Shared bedding and inadequate laundry facilities can contribute to rapid transmission.
How to Treat Scabies: Getting the Right Medical Help
If you suspect you have scabies, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Effective treatment involves medicated creams and lotions that kill the mites and their eggs. Prescription medications, such as permethrin cream or oral ivermectin, are typically recommended by healthcare professionals.
1. Prescription Creams and Lotions
Your doctor may prescribe a topical treatment that should be applied over the entire body, from the neck down. The cream must be left on for a specific duration, usually overnight, to ensure that the mites are eliminated. It’s common to experience itching for a few weeks even after successful treatment, as the body clears away the remaining mite debris.
2. Home Remedies and Preventive Measures
While prescription medication is essential, there are steps you can take at home to prevent reinfection:
- Wash bedding, towels, and clothing in hot water (at least 60°C) to kill any remaining mites.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals until treatment is complete.
- If certain items can’t be washed in hot water, seal them in a plastic bag for three days to suffocate the mites.
Dealing with the Stigma: Don’t Let Scabies Go Untreated
Despite the stigma associated with scabies, it’s important to understand that anyone can catch it. Professor Kamila Hawthorne of the Royal College of General Practitioners emphasizes that the social stigma surrounding scabies should not prevent people from seeking medical help. Untreated scabies not only worsens the condition but also increases the risk of transmission to others.
Complications of Untreated Scabies: Why You Should Act Fast
While scabies itself is not life-threatening, ignoring it can lead to serious complications. Constant scratching can result in open sores, which may become infected with bacteria, leading to impetigo, cellulitis, or even more severe skin infections. Additionally, untreated scabies can worsen existing skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, making them harder to manage.
Conclusion: Take Tiny Red Dots Seriously
The appearance of tiny red dots on your arms or hands shouldn’t be dismissed, as they could be an early warning sign of scabies. Prompt treatment is essential not only to alleviate the discomfort but also to prevent the spread to others. Whether you’re a student, a parent, or someone living in close quarters with others, awareness and early action can make all the difference. Don’t let stigma keep you from addressing the issue—your health, and that of those around you, depends on it.